7.7
A metal bar of mass m slides frictionlessly on two parallel conducting rails a
distance l apart (Fig 7.16). A resistor R is connected across the rails
and a uniform magnetic field B, pointing into the page, fills the entire region.
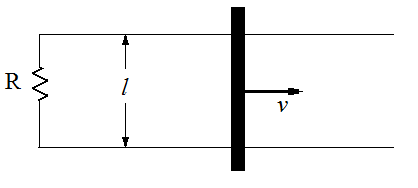
Figure 7.16
-
If the bar moves to the right at a speed v, what is the current in the resistor?
In what direction does it flow?
-
What is the magnetic force on the bar? In what direction?
-
If the bar starts out with a speed vo at time t = 0, and is left to slide,
what is its speed at a later time t?
-
The initial kenitic energy of the bar was, of course,
0.5 mvo2.
Check to see that the energy delivered to the resistor is exactly
0.5 mvo2.

