6.12
An infinitely long cylinder of radius R, carries a "frozen-in",
magnetization parallel to its axis.
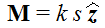
where k is a constant and s is the distance from the axis;
there are no free electrons anywhere.
Find the magnetic field inside and outside the cylinder by two different methods:
- As in Sect. 6.2, locate all the bound currents, and calculate the field they produce.
-
Use Ampere's law (in the form of Eq. 6.20) to find H,
and then get B from Eq.6.18. (Notice that the second method is much faster,
and avoids any explicit reference to the bound currents.)