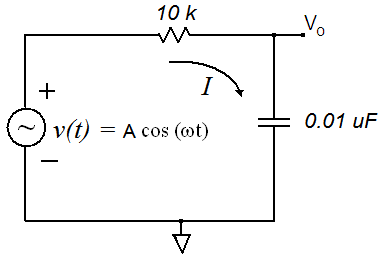
Figure 2 The Function Generator provides source voltage V. The
oscilloscope displays the input and output voltages,
Figure 3 The oscilloscope, Function Generator and circuit board are shown,
Figure 4 The oscilloscope displays the input voltage, V,
and the output voltage, Vo. The output is delayed by
q degrees. For the case shown
q
is about 60o.